Gauchersymptoms.me
Genetics
How is Gaucher disease inherited?
Gaucher disease is not contagious, but it is a hereditary condition that can be passed down from parents to their children.1
Every cell in the human body contains chromosomes – thread-like structures carrying genetic information – that exist as pairs. One chromosome in each pair is inherited from the mother, and the other from the father. For each gene, a person therefore inherits one copy (allele) from each parent.1 The gene responsible for Gaucher disease is found on chromosome 1.2
For a person to have the disease, both copies of this chromosome (one inherited from each parent) must contain a mutated version of the Gaucher disease gene. This is called autosomal recessive inheritance.1 (condition caused by having a mutation/change in both copies of a gene)
A person who has one chromosome containing a mutated Gaucher disease gene and one chromosome containing a normal gene will not develop Gaucher disease. This type of person is called a carrier.1
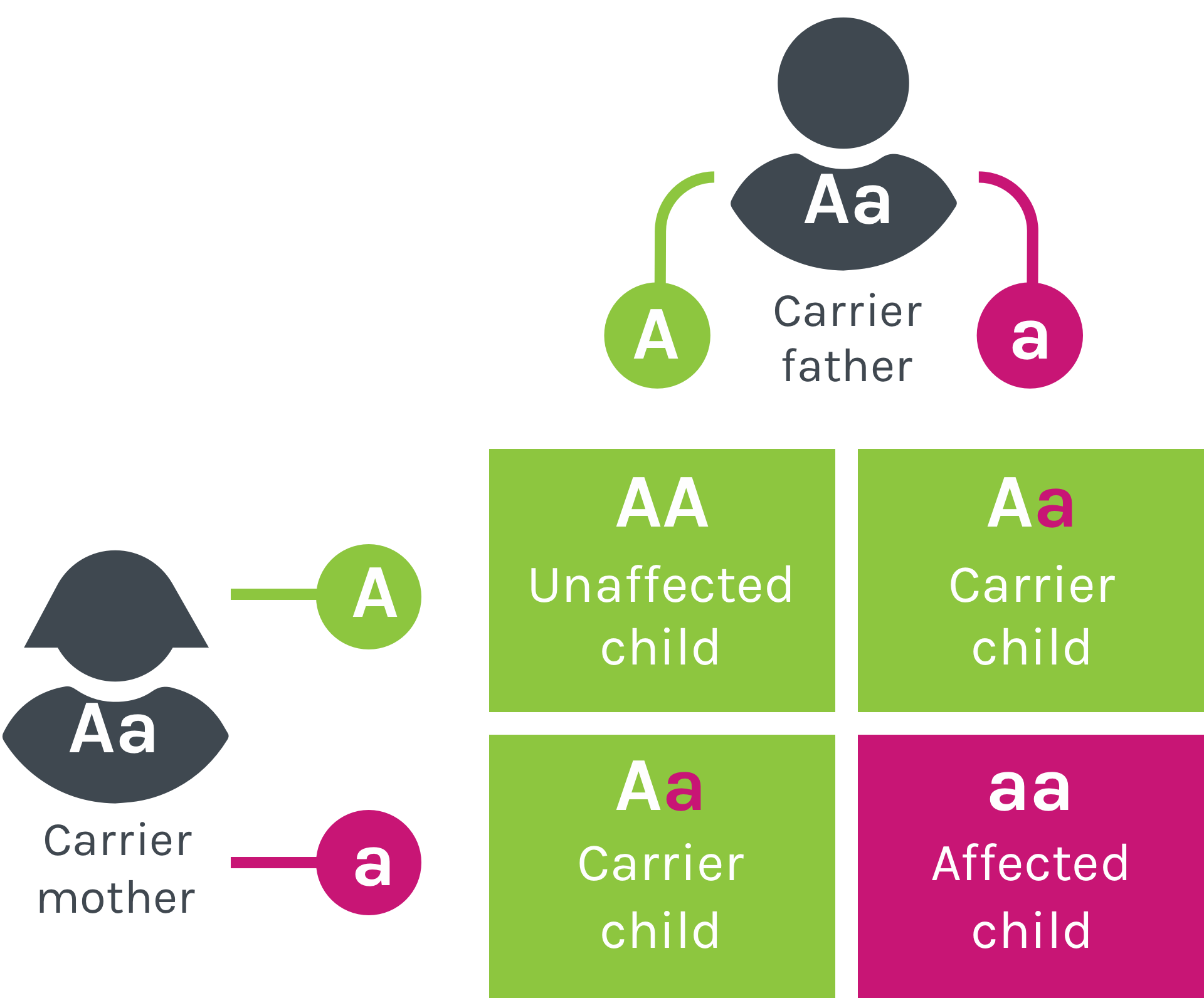
If both parents are carriers of Gaucher disease (each parent has one Gaucher disease mutated gene, ‘a’, and one normal gene, ‘A’), each pregnancy carries the following risks:1
A 25% chance (1 in 4) that the child will inherit two normal copies of the gene (A), and will therefore be unaffected by Gaucher disease.
A 50% chance (2 in 4) that the child will inherit only one copy of the mutated gene (a), and will therefore be a carrier.
A 25% chance (1 in 4) that the child will inherit two copies of the mutated Gaucher disease gene (a), and will therefore develop Gaucher disease.
Autosomal recessive inheritance1 (condition caused by having a mutation/change in both copies of a gene)